What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease in which blood sugar levels are above normal. An organ in our body called the pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Insulin helps control the sugar level in your blood and help glucose to get into the cells of our bodies. Glucose is the main energy source for our cells. Even though you have high levels of it in your blood, your body cannot make use of it without insulin. In short, your cells are starving even though you have abundant energy source.
 |
| diabetes is having too much sugar in your blood |
What are the types of diabetes?
There are two types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes, previously known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) or juvenile-onset diabetes, account for about 5% of all diabetes cases. In this type of diabetes, the cells of the pancreas can no longer make insulin because the body's immune system has destroyed them. Type 2 diabetes, previously known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult-onset diabetes, account for about 90% to 95% of all diabetes cases. This type of diabetes usually begins with insulin resistance in which the body can not properly use insulin. Over time the pancreas loses the ability to secrete enough insulin in response to meals.
What are the risk factors for diabetes?
- Being overweight or obese.
- Having a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes.
- Being African American, American Indian, Asian American, Pacific Islander, or Hispanic American/Latino heritage.
- Having a prior history of diabetes in pregnancy or birth of at least one baby weighing more than 9 pounds.
- Having high blood pressure measuring 140/90 or higher.
- Having abnormal cholesterol with HDL ("good") cholesterol is 35 or lower, or triglyceride level is 250 or higher.
- Being physically inactive—exercising fewer than three times a week.
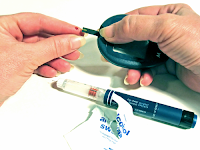 |
| blood sugar monitor |
When should I be tested for diabetes?
Anyone aged 45 years or older should consider getting tested for diabetes, especially if you are overweight. If you are younger than 45, but are overweight and have one or more additional risk factor, you should consider getting tested.
What are the symptom of diabetes?
Many people have no signs or symptoms of diabetes. The symptoms can also be very vague that you might not notice them until you have suffered the complications. Initial signs of diabetes are
- increased thirst
- increased hunger
- fatigue
- increased urination, especially at night
What is the treatment for diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is treated by healthy eating, exercise, and insulin injections. For type 2 diabetes, the treatment consists of healthy eating, exercise, routine blood glucose testing. In addition, people with type 2 diabetes often requires oral medication, insulin, or both to control their blood sugar levels.
People living with diabetes may see endocrinologists, who may specialize in diabetes care; ophthalmologists for eye examinations; podiatrists for routine foot care; and dietitians and diabetes educators who teach the skills needed for daily diabetes management.